波长导向的自主光驱动分子马达的定向旋转
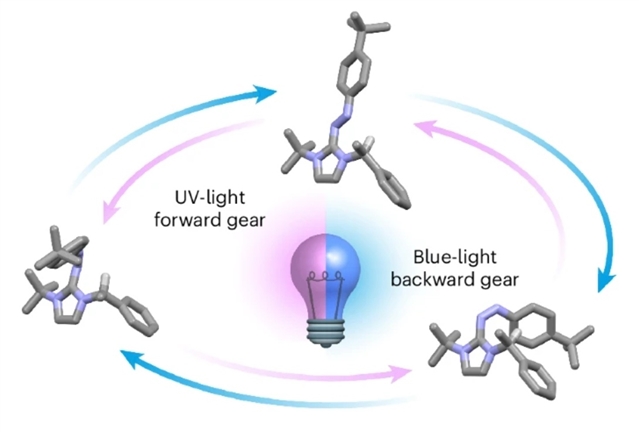
近日,意大利博洛尼亚大学Curcio, Massimiliano团队研究了波长导向的自主光驱动分子马达的定向旋转。2026年1月28日,《自然-化学》杂志发表了这一成果。
人工分子马达凭借其能在分子尺度上实现定向控制运动的能力,成为纳米技术研究的前沿领域。光驱动纳米马达的开发尤其具有挑战性,对开发太阳光驱动系统与活性材料具有重要潜力。
研究组报道了一种偶氮咪唑鎓光化学分子旋转马达,该马达通过三角形反应循环运行,利用光异构化过程中非对映异构体的形成实现运动。这些非对映异构体不同的热稳定性与光化学反应性,使得净定向运动得以实现:该运动结合了围绕C–N单键的热旋转与两个主要通过旋转机制实现的光诱导构型重排(计算研究证实了这一点)。通过改变照射波长,可调节持续光照下所得耗散态的组成,从而实现马达旋转方向的逆转。
附:英文原文
Title: Wavelength-steered directional rotation in an autonomous light-driven molecular motor
Author: Nicoli, Federico, Taticchi, Chiara, Lorini, Emilio, Borghi, Sara, Aleotti, Flavia, Silvi, Serena, Credi, Alberto, Garavelli, Marco, Muccioli, Luca, Baroncini, Massimo, Curcio, Massimiliano
Issue&Volume: 2026-01-28
Abstract: Artificial molecular motors are at the forefront of research in nanotechnology due to their ability to perform tasks by harnessing directionally controlled motion at the molecular scale. The development of light-driven nanomotors is a particularly challenging task that holds great potential for the development of sunlight-powered systems and active materials. Here we describe an azoimidazolium photochemical molecular rotary motor which operates along a triangular reaction cycle exploiting the formation of diastereomeric species upon photoisomerisation. The different thermal stability and photochemical reactivity of these diastereomers permit net directional motion combining a thermal rotation about a C–N single bond and two light-induced configurational rearrangements that proceed predominantly through a rotational mechanism, as corroborated by computational studies. The composition of the dissipative state obtained upon continuous supply of light can be modified by changing the irradiation wavelength, and as a result, the preferred rotation direction of the motor is inverted.
DOI: 10.1038/s41557-025-02045-x
Source: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41557-025-02045-x



